Function of heart
What is the heart’s function?
Your heart’s main function is to move blood throughout your body. Your heart also:
- Controls the rhythm and speed of your heart rate.
- Maintains your blood pressure.
How does your heart work with other organs?
Your heart works with other body systems to control your heart rate and other body functions. The primary systems are:
- Nervous system: Your nervous system helps control your heart rate. It sends signals that tell your heart to beat slower during rest and faster during stress.
- Endocrine system: Your endocrine system sends out hormones. These hormones tell your blood vessels to constrict or relax, which affects your blood pressure. Hormones from your thyroid gland can also tell your heart to beat faster or slower.
ANATOMY
Where is your heart located?
Your heart is located in the front of your chest. It sits slightly behind and to the left of your sternum (breastbone). Your ribcage protects your heart.What side is your heart on?
Your heart is slightly on the left side of your body. It sits between your right and left lungs. The left lung is slightly smaller to make room for the heart in your left chest.
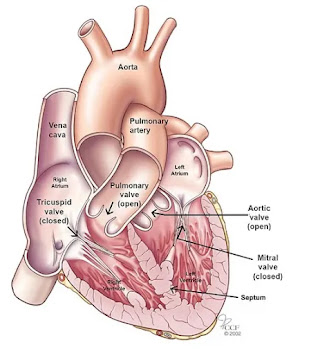
- Left anterior descending artery (LAD): Supplies blood to the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum.
- Right coronary artery (RCA): Supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum.
Electrical conduction system
Your heart’s conduction system is like the electrical wiring of a house. It controls the rhythm and pace of your heartbeat. It includes:
- Sinoatrial (SA) node: Sends the signals that make your heart beat.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node: Carries electrical signals from your heart’s upper chambers to its lower ones.
Your heart also has a network of electrical bundles and fibers. This network includes:
- Left bundle branch: Sends electric impulses to your left ventricle.
- Right bundle branch: Sends electric impulses to your right ventricle.
- Bundle of His: Sends impulses from your AV node to the Purkinje fibers.
- Purkinje fibers: Make your heart ventricles contract and pump out blood.
- External links
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21704-heart#:~:text=Your%20heart's%20main%20function%20is,Maintains%20your%20blood%20pressure.
Comments
Post a Comment